BlueCheck® is a detection tool that enables identification of early-stage tooth decay, allowing a prevention approach to heal and preserve the natural tooth structure.
BlueCheck aids oral health professionals to visualize active caries in enamel and dentin.
BlueCheck makes it possible to detect caries lesions early. This means minimally invasive dentistry approach and cost-effective repair treatments can be used – before cavities develop – potentially preventing painful and expensive surgical dentistry options.
Visual evidence of disease
Simplifies early caries detection with a high contrast blue color at the sites of demineralization to aid visualization of early caries.
Fast and easy to use
With only five simple steps, procedure is less than a few minutes.
It requires no capital equipment, standard armamentarium.
Specific for active caries
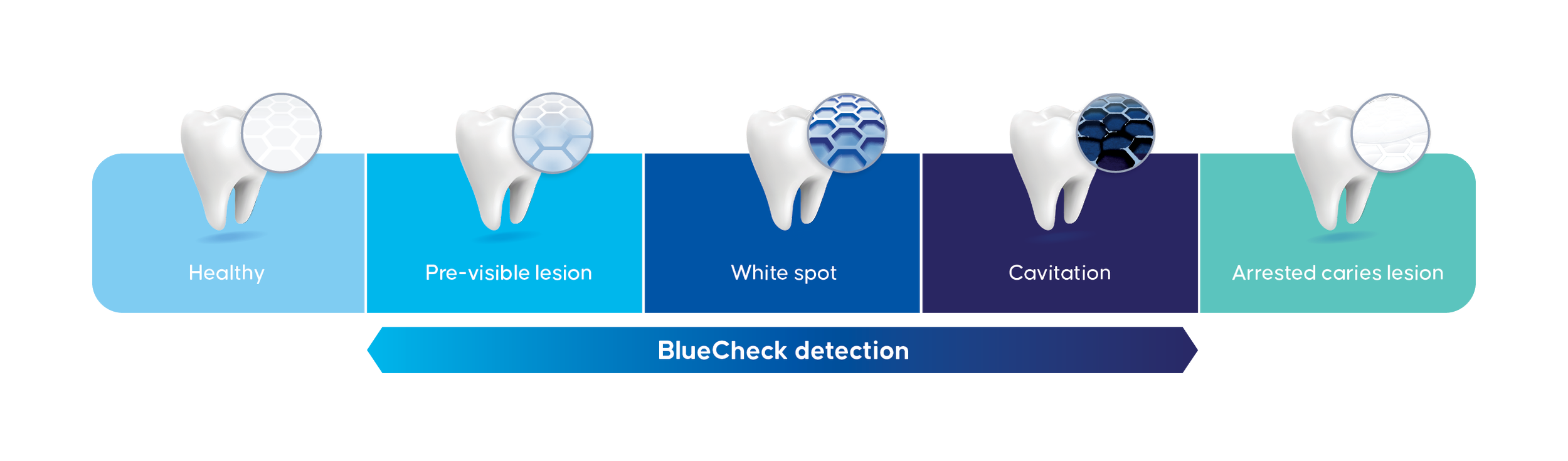
BlueCheck specifically binds to surface and sub-surface porosity associated with active caries lesions and turns them blue.
Healthy enamel, arrested caries lesions and exposed root surfaces do not turn blue.
Sensitive detection
BlueCheck can detect lesions as shallow as ~50 microns deep, compared to an radiograph’s detection limit of ~200-400um.
BlueCheck Detection
Objective blue colour at sites of demineralization, does not turn healthy enamel or arrested lesions blue.
The science behind BlueCheck
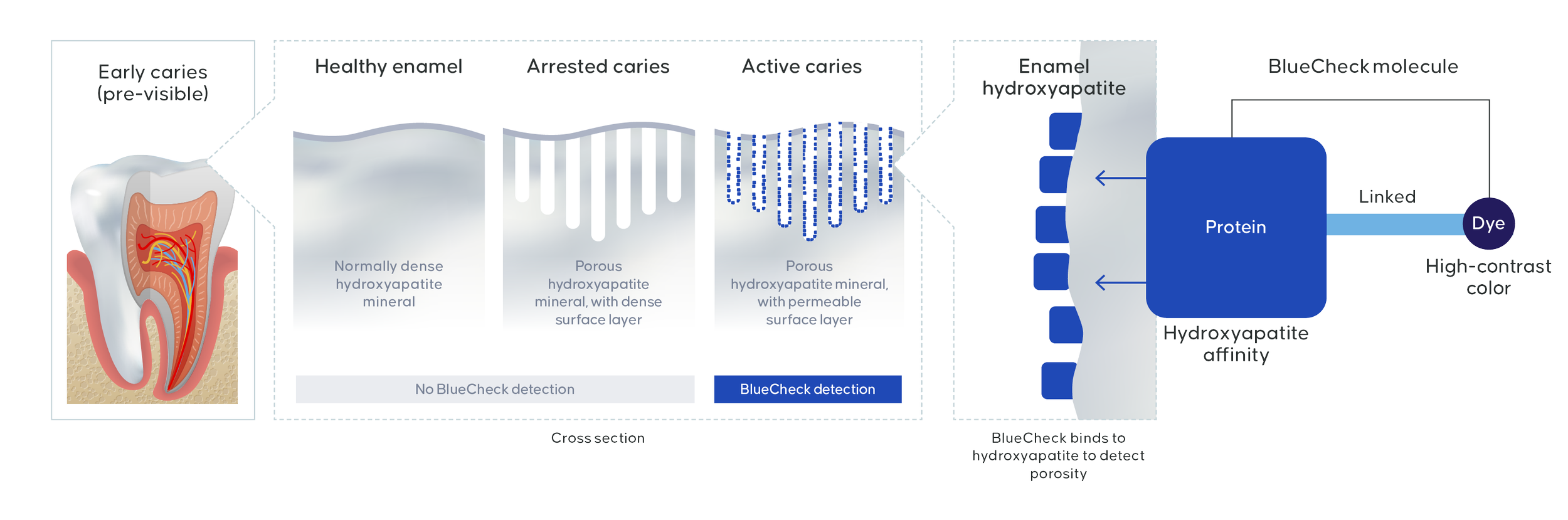
Some proteins have a high affinity for the hydroxyapatite that is exposed at sites of dental demineralization. This discovery was used to develop a saline-based caries detection and monitoring device. BlueCheck is a solution containing a biomolecule linked to a dye that binds to the hydroxyapatite exposed in caries lesions. It is designed to give clinicians a direct measure of porosity and disease status.
BlueCheck is applied to the tooth surface, through an electrostatic interaction it binds to hydroxyapatite, after rinsing to wash away any unbound BlueCheck, the remaining blue color is indicative of dental porosity. The deeper the lesion, the more porous area exposed and the darker the blue color (as there is more hyrdroxyapatite for BlueCheck to bind to). Removal of BlueCheck by cleaning with SLS-toothpaste and/or interaction with saliva.
BlueCheck Mode of Action
BlueCheck utilises the natural hydroxyapatite-binding chemistry of proteins to specifically and reversibly bind to porous dental hydroxyapatite, enabling direct visualization of dental caries.
Healthy enamel and arrested lesions have little exposed hydroxyapatite for BlueCheck to bind to.
Benefits of BlueCheck to clinical practice
When used during routine dental examinations, BlueCheck helps clinicians:
Patient education tool
Blue color highlights problem areas providing education tool and motivator for patients to improve oral hygiene.
Supports case acceptance
Clear visual evidence supports patient’s understanding treatment plan recommendations and enhances treatment acceptance.
Monitor disease over time
A digital image can record the blue color and BlueCheck can be used to monitor the progress of any intervention.
Enhance oral care outcomes
By catching active caries lesions early, allows a tissue preserving approach to caries management.
Align standard of care
Delivers clinical consistency through an objective visual read-out at active demineralization sites. Allows for standardization of detection and preventive treatment approaches.
Build trust, fostering patient loyalty
BlueCheck’s blue color of the tooth surface provides objective, visual evidence to support the clinician’s diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Reimbursement for a Procedure using BlueCheck
CDT Code D0600, for reimbursement
“Non-ionizing diagnostic procedure capable of assessing and documenting changes in the structure of enamel, dentin, and cementum.”
American Dental Association (ADA) CDT Code
The procedure may be performed within and enhance other dental codes within caries management environment.
Such as routine patient dental examination, caries risk assessment (D0601-603), nutrition counselling (D0130), oral hygiene instruction (D1330), counselling around dry mouth (D1321), radiographs, dispensing medicaments for home use (D9630) and a number of other procedures such as prophylaxis clean, preventive applications (Fluoride Varnish D1206, D1208, Dental Sealant (per tooth) D1351, Interim Caries Arresting Medicament (per tooth) D1354, Caries Prevention Medicament D1355) and restoration (Hydroxyapatite Regeneration Medicament(per tooth) D2991) procedure codes.
We acknowledge that dental codes and their usage and coverage vary between States and different dental insurance plans. Please check with your dental benefit’s program for the most suitable code(s).
Mangum J et al. (2010) Surface Integrity Governs the Proteome of Hypomineralized Enamel. J Dent Res 89(10):1160-1065.
Jablonski-Momeni A, et al. (2022) Ability of BlueCheck liquid stain as a novel technology to detect initial enamel demineralization. Car Res2; 56:555-565.
Lippert F, et al. (2023) Detection of Artificial Enamel Caries-like Lesions with a Blue Hydroxyapatite-Binding Porosity Probe. J of Dent, 135:104601.
Poster: Mascarenhas R, et al. Investigation of a novel diagnostic for early detection of white spot lesions. ASO, March 2022.
Poster: Lippert F, et al. Investigating the ability of a blue dye to selectively stain early enamel caries lesions. ORCA, July 2022.
Poster: Jablonski-Momeni A, et al. In-vitro performance of BlueCheck liquid as a novel technology for detection of initial enamel demineralization. ORCA, July 2022.
BlueCheck Instructions for Use, IFU-B11040 REV: V3, 05/2023. 001865.
American Dental Association (ADA) CDT Code Dental Procedures and Nomenclature, https://www.ada.org/publications/cdt.